Overview
- Brief Narrative
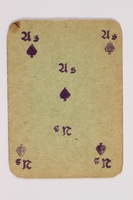
- Two decks of 32 skat playing cards made in Brunnlitz slave labor camp from handcut rubber stamps by an unnamed prisoner and saved by fellow prisoners Heinz and Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany, to Krakow, Poland. In September 1939, Poland was occupied by Germany. In May 1941, the Dresslers were forced into the Jewish ghetto. Heinz did forced labor for construction of Krakow-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the ghetto was liquidated and the Dressler's were sent to the camp, a brutal place where Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. Heinz worked in the camp office; Martha and Susi in a factory; Joachim outside the camp. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler owned two nearby factories and employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. The family got on the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans prepared to close the camp. Schindler relocated his factory to Brunnlitz in German occupied Czechoslovakia, designated a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. Schindler kept the Germans out of the camp. Schindler left on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps trying to find a place they wanted to stay. In February 1947, they emigrated to the United States.
- Date
-
use:
1944 October-1945 May
- Geography
-
creation:
Brünnlitz (Concentration camp);
Brněnec (Czech Republic)
- Credit Line
- United States Holocaust Memorial Museum Collection, Gift of Diane Spiegel Belok and Donna Kantor Krasner
- Contributor
-
Subject:
Henry Dressler
- Biography
-
Henry Dressler (born Heniz, 1919-2005) was born on October 22, 1919, in Dresden, Germany, to Joachim (1888-1971) and Martha Miriam (1896-1956) and had one sister, Susi (1914-1954). Joachim served in the Austro-Hungarian Army in World War I. Joachim owned a textile factory that manufactured linen tablecloths, sheets, and other textiles and had five to ten employees. Martha assisted him with the business. The family was moderately observant and Heinz attended Hebrew school.
In 1933, the Nazi dictatorship assumed power in Germany and enacted a series of anti-Jewish policies. Joachim’s brother, Ferdinand, closed his office in Berlin on April 1, 1933, and left for Palestine. Many Jews were forced to put non-Jews in charge of their businesses or sell them at a loss to Nazi approved buyers, but Joachim’s business was never Aryanized in this way. The family considered leaving Germany, possibly for the US, but the strict quotas made getting visas unlikely. In 1936, Henry was forced to leave school because he was Jewish. He attended a private school run by the Dresden Chamber of Commerce. He participated in some school activities, such as orchestra, but as a Jew, could not go on school outings, or participate in activities, such as sports, that took place in public spaces. He then got an internship with a private, Jewish-owned bank and was promoted, until 1938, when the bank was Aryanized. Henry then got a job with a luxury department store, Hirsch & Co. In October 1938, the family was taken to police headquarters and their passports were invalidated. They were taken to the railway station in open trucks to shame them publicly and deported to Poland along with 1500 other Jews. Because Joachim was not born in Germany and did not have German citizenship, the family was considered stateless.
Joachim recalled that some family members lived in Krakow, Poland and the family was welcomed there by the Wasserberger family. They had a large house and converted the gym into a bedroom. Henry got a job with an import firm handling correspondence. On September 1, 1939, Germany began bombing Krakow and the city fell after 3 days. The Wasserbergers fled east, eventually reaching New York. The house was occupied by the German Army commandant, but Henry and his family were allowed to remain. In May 1940, the Germans began expelling Jews to the countryside. In March 1941, they forced Krakow’s Jews to move into a ghetto where they lived in a set of small rooms. The Germans opened several factories in the ghetto staffed by forced labor. As Henry spoke German, he was able to get a job with the Jewish Council as a typist. Food was scarce. During one of the frequent aktions when Jews were rounded up for deportation, a German officer who knew Henry came over and asked what they were doing there. They then were moved to another spot and sent home. Henry witnessed Germans throwing children out of the windows of an orphanage on the square on one occasion. Henry’s mother worked in a brush factory owned by Joseph Madrich who provided the family with food. His father and sister had office jobs.
In 1942, Henry was assigned to a labor detail to construct Krakow- Płaszów labor camp. The site included a Jewish cemetery and tombstones were broken to use as paving stones. Workers had to assemble in the square several times a day to be counted. Henry collapsed one day and was taken to hospital. The Krakow ghetto was liquidated on March 13, 1943, and his family was sent to the camp. Henry worked in the camp office and Martha and Susi worked night shifts in clothing factories. Susi also had an office job and Joachim worked outside the camp. Henry saw his father often, but rarely saw his mother and sister.
In August 1944, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran an enamelware and an armament factory nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached in the summer of 1944, the Germans began to plan to dismantle Płaszów. Schindler arranged to move his factory to Brünnlitz in the Moravia region of German occupied Czechoslovakia. On October 15, Joachim and Henry were transported to Schindler’s new factory. Henry was given prisoner number 69046. They were transferred to Brünnlitz, a day’s march from the rail station. They worked in a textile plant that had been converted into an ammunition factory. Martha and Susi were transported from Płaszów on August 21, and arrived in Brünnlitz on November 14. Henry worked in Schindler’s office as a cost accountant. Days began at 6am with roll call, breakfast, and then work. Henry remembered Emilie Schindler helping in the sick bay and trying to get food and medicine. Schindler kept German camp personnel from entering Brünnlitz and did his best to provide food. Henry began to keep a diary in German shorthand on April 22, 1945. Schindler left the camp on May 7, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated by Soviet forces on May 9.
The Dressler family left for Prague, where Czech people helped them get food and clothing. They spent the next several months traveling to transit camps in Italy and Austria, trying to find a place where they wanted to stay. At the end of September, they went to the home of an Italian solder from Rome whom they had met in June. He was not there, but his wife let the family stay for two months. Henry got a job as an office clerk with the British Army. Henry had corresponded with an American girl in 1937 and 1938 and she helped the family get an affidavit of support for a US visa. They arrived in the US on February 20, 1947.
Henry got a job in a family business that distributed photographic supplies. In 1957 he met Martha Ohsie in 1957 and soon married. They had no children and lived in Newark, New Jersey. Henry rarely talked of his experiences, but he did testify at a war crimes tribunal in the 1960s. When the book Schindler’s List, by Thomas Keneally was published in 1982, he sent copies to friends with a note explaining that he knew many of the people and places from his own experience and that he and his family had survived due to the kindness of Schindler and others. After he saw the film, Schindler’s List, in 1993, he began to tell his story to school and civic groups. He often took his striped concentration camp uniform to show during the talks.
Physical Details
- Language
- German
- Classification
-
Toys
- Category
-
Games
- Object Type
-
Playing cards (lcsh)
- Genre/Form
- Playing cards.
- Physical Description
- a-bl. Two decks of handmade, rectangular, paper, skat cards. Each deck contains 32 cards, 8 for each suit: red hearts, red diamonds, black clovers, and black spades. Each number card has the number in each corner with the suit symbol below, and the corresponding number of symbols in the center. The Jack card has a B in each corner, and Bube, German for Jack, in mirror image. The Queen card has a D in each corner and Dame, [Queen], in mirror image. The King card has a K in each corner and Konig [King], in mirror image. The Ace card has As in each corner and in the center above the suit symbol.
a-h. Black spade suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: a-d. 7-10 spades; e. Ace; f. Jack; g. Queen; h. King.
i-p. Black spade suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: i-l. 7-10 spades; m. Jack; n. Queen; o. King; p. Ace.
q-x. Red heart suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: q-t. 7-10 hearts; u. Jack; v. Queen; w. King; x. Ace.
y-af. Black clover suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: y.-ab. 7-10 clovers; ac. Jack; ad. Queen; ae. King; af. Ace.
ag-an. Red heart suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: ag-aj. 7-10 hearts; ak. Jack; al. Queen; am. King; an. Ace.
ao-av. Red diamond suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: ao-ar. 7-10 diamonds; as. Jack; at. Queen; au. King; av. Ace.
aw-bd. Red diamond suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: aw-az. 7-10 diamonds; ba. Jack; bb. Queen; bc. King; bd. Ace.
be-bl. Black clover suit of 8 cards: 4 number and 4 face cards: be-bh. 7-10 clovers; bi. Jack; bj. Queen; bk. King; bl Ace. - Dimensions
- overall: Height: 3.125 inches (7.938 cm) | Width: 2.375 inches (6.033 cm)
- Materials
- overall : paper, ink
Rights & Restrictions
- Conditions on Access
- No restrictions on access
- Conditions on Use
- No restrictions on use
Keywords & Subjects
- Topical Term
- Concentration camp inmates--Czech Republic--Brnenec--Biography. Concentration camp inmates--Poland--Plaszow--Biography. Holocaust, Jewish (1939-1945)--Poland--Kraków--Personal narratives, Jewish. Holocaust survivors--United States--Biography. Righteous Gentiles in the Holocaust--Biography. World War, 1939-1945--Jews--Rescue--Personal narratives. Forced labor.
- Geographic Name
- Brněnec (Czech Republic) Dresden (Germany) Kraków (Poland) Prague (Czech Republic) Rogoźnica (Województwo Dolnośląskie, Poland)
- Personal Name
- Schindler, Oskar, 1908-1974.
Administrative Notes
- Legal Status
- Permanent Collection
- Provenance
- The playing cards were donated to the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in 2013 by Diane Spiegel Belok and Donna Kantor Krasner, the nieces of Henry Dressler.
- Funding Note
- The cataloging of this artifact has been supported by a grant from the Conference on Jewish Material Claims Against Germany.
- Record last modified:
- 2023-02-23 16:44:49
- This page:
- https://collections.ushmm.org/search/catalog/irn95287
Also in Henry Dressler family collection
The collections consists of two concentration camp uniforms, knit caps, a set of playing cards, correspondence, documents, clippings, negatives, photographs, and video tapes relating to the experiences of Heinz, Joachim, Martha, and Susi Dressler, originally from Dresden, Germany, in the Brunnlitz factory in Moravia operated by Oskar Schindler during the Holocaust which they all survived by being placed on Schindler's list, and also their postwar experiences following their emigration to the United States.

Handmade metal knife used by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Knife with a coil handle made in Brunnlitz labor camp by Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany to Kraków, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Kraków-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Kraków ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That same year in August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran factories nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until immigrating to the US in February 1947.

Handmade metal comb used by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Metal comb made in Brunnlitz labor camp by Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany to Kraków, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Kraków-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Kraków ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That same year in August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran factories nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until immigrating to the US in February 1947.

Pocket mirror used by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Hand mirror used by Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany to Kraków, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Kraków-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Kraków ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That same year in August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran factories nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until immigrating to the US in February 1947.

Drawing
Object

Drawing
Object

Drawing
Object
Concentration camp uniform jacket and pants worn by an inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Concentration camp uniform worn by Heinz Dressler's father, Joachim Dressler, marked with the prisoner number 69046. In October 1938, Heinz, his sister, Susi, and parents, Joachim and Martha, were deported from Dresden, Germany to Kraków, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to Kraków’s Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Kraków-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Kraków ghetto and Heinz's family members were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the guards arbitrarily shot inmates daily. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That same year in August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran an enamelware and an armament factory nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, whom he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated on May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until immigrating to the US in February 1947.
Concentration camp uniform jacket and pants worn by an inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Concentration camp uniform worn by Heinz Dressler, marked with the prisoner number 69454. In October 1938, Heinz, his sister, Susi, and parents, Joachim and Martha, were deported from Dresden, Germany to Kraków, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to Kraków’s Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Kraków-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Kraków ghetto and Heinz's family members were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the guards arbitrarily shot inmates daily. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That same year in August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran an enamelware and an armament factory nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, whom he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated on May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until immigrating to the US in February 1947.
Green knit cap worn by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Green knit concentration camp uniform cap worn by Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany, to Krakow, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Krakow-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Krakow ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran factories nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until emigrating to the US in February 1947.
Green knit cap worn by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Green knit concentration camp uniform cap worn by Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany, to Krakow, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Krakow-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Krakow ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran factories nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until emigrating to the US in February 1947.
Maroon handkerchief with acorns used by a concentration camp inmate saved by getting on Schindler's list
Object
Maroon handkerchief with acorns found inside the prisoner uniform of Heinz or Joachim Dressler. In October 1938, the Dressler family, Joachim, wife, Martha, and children Susi, 24, and Heinz, 19, were deported from Dresden, Germany, to Krakow, Poland. Germany occupied Poland in September 1939. In May 1941, the Dresslers were sent to the Jewish ghetto. In 1942, Heinz was a forced laborer sent to construct Krakow-Płaszów labor camp. In March 1943, the Germans liquidated the Krakow ghetto and Heinz's family were sent to the camp. Płaszów was a brutal camp where the Ukrainian guards daily shot inmates for no reason. In 1944, Płaszów became a concentration camp and conditions worsened. That August, the family learned of Oskar Schindler’s list. Schindler was a German businessman who ran an enamelware and an armament factory nearby. He employed about 900 Jewish forced laborers, who he protected from the abuse at Płaszów and from deportation. Heinz knew Izak Stern, who worked for Schindler. The family was able to get added to the list, partly because they spoke German. As the Soviet Army approached, the Germans decided to dismantle the camp. Schindler arranged to relocate his factory to Brunnlitz in Czechoslovakia as a subcamp of Gross Rosen. In October 1944, Heinz and Joachim were transported to Gross Rosen, and sent to Brunnlitz. Martha and Susi arrived in November. They worked in Schindler's ammunition plant. Schindler kept German camp personnel out of the camp and did his best to feed the inmates. Schindler left the camp on May 7, 1945, the day Germany surrendered. The camp was liberated May 9 by Soviet troops. The family left for Prague, then traveled to different transit camps until emigrating to the US in February 1947.